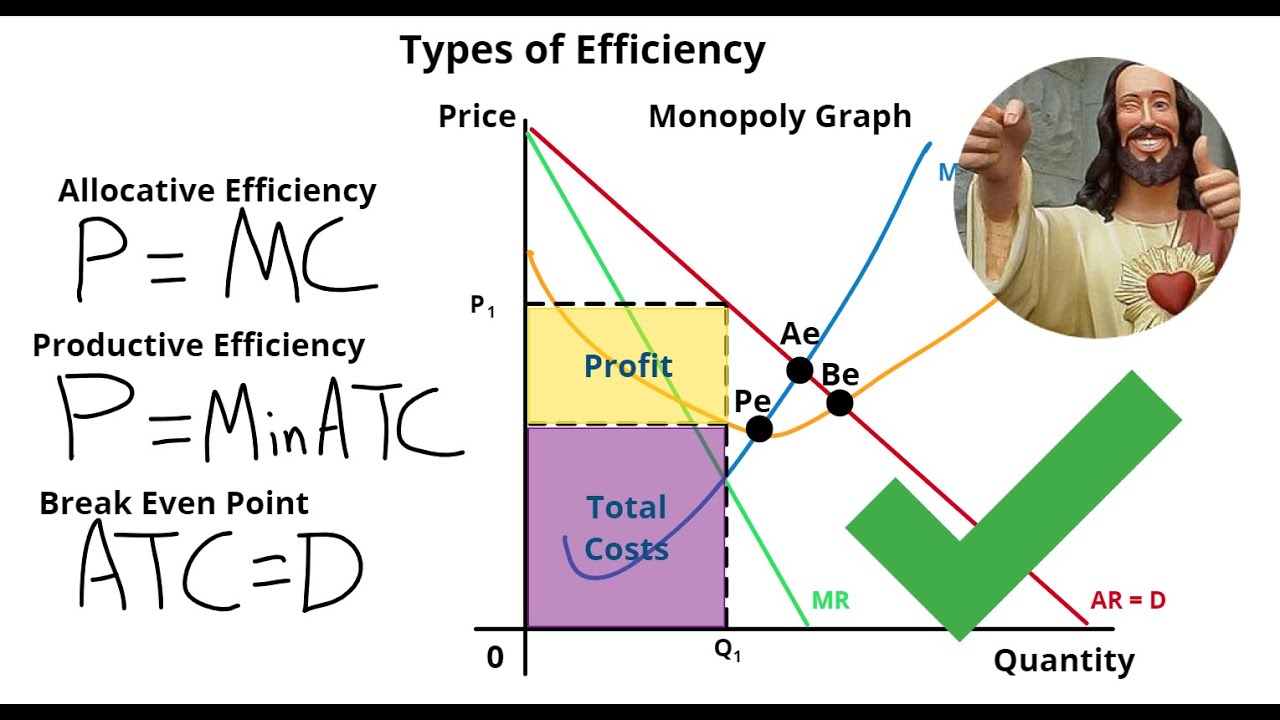
In the realm of economics, efficiency plays a pivotal role in determining how resources are allocated and utilized. Two essential concepts that often come into play are allocative efficiency and productive efficiency. These two forms of efficiency are vital for understanding how an economy operates and serves its citizens, impacting everything from the prices of goods and services to the overall economic health of a nation. While both concepts focus on the optimal use of resources, they approach the idea of efficiency from different angles. Allocative efficiency involves the distribution of resources in a way that maximizes social welfare, while productive efficiency is concerned with minimizing costs and maximizing output. In this article, we will delve deeper into these two concepts, exploring their differences, implications, and real-world applications.
To truly grasp the significance of allocative efficiency vs productive efficiency, it is crucial to understand their definitions and frameworks. Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are allocated in such a way that the last unit produced adds as much to consumer satisfaction as it costs to produce. In contrast, productive efficiency is achieved when goods are produced at the lowest possible cost, maximizing output while minimizing inputs. These efficiencies are not mutually exclusive; rather, they complement each other in striving for an optimal economic environment.
As we navigate through this intricate relationship between allocative efficiency and productive efficiency, we will address several key questions that arise, helping to clarify their respective roles within the economy. By understanding these concepts, policymakers, businesses, and consumers can make more informed decisions that contribute to the overall well-being of society.
What is Allocative Efficiency?
Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed in a manner that maximizes the total benefit to society. This efficiency is achieved when the price of a good reflects the marginal cost of producing it, ensuring that consumer preferences are met without overproduction or underproduction.
How is Allocative Efficiency Measured?
Allocative efficiency can be measured using the concept of consumer surplus and producer surplus. Consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay. Producer surplus, on the other hand, is the difference between the price producers receive and the minimum price they are willing to accept. When both surpluses are maximized, allocative efficiency is achieved.
Why is Allocative Efficiency Important?
Allocative efficiency is crucial for several reasons:
- It ensures optimal resource allocation, enhancing overall societal welfare.
- It promotes competition among producers, leading to innovation and better products.
- It minimizes waste, as resources are directed towards the production of goods that are most valued by consumers.
What is Productive Efficiency?
Productive efficiency is achieved when goods and services are produced at the lowest possible cost. This concept focuses on minimizing waste and ensuring that resources are used effectively to produce the maximum output.
How is Productive Efficiency Achieved?
Productive efficiency can be achieved through various means:
- Adopting advanced technologies to improve production methods.
- Streamlining processes to reduce labor and material costs.
- Enhancing worker productivity through training and skill development.
Why is Productive Efficiency Important?
Productive efficiency is vital for several reasons:
- It lowers production costs, leading to lower prices for consumers.
- It allows businesses to maximize profits, enabling reinvestment and growth.
- It enhances competitiveness in the global market.
How Do Allocative Efficiency and Productive Efficiency Interact?
The relationship between allocative efficiency vs productive efficiency is intricate. While both are essential for a well-functioning economy, they can sometimes be at odds. For instance, a firm may produce goods at a low cost (productive efficiency) but may not be producing the types of goods that consumers want (allocative efficiency).
Can a Firm Be Allocatively Efficient but Not Productively Efficient?
Yes, a firm can achieve allocative efficiency by providing products that meet consumer demand, even if it does so at a higher cost. For example, a luxury brand may produce high-quality goods that consumers are willing to pay a premium for, despite the higher production costs involved.
Can a Firm Be Productively Efficient but Not Allocatively Efficient?
Conversely, a firm may be productively efficient by minimizing its production costs, yet fail to meet consumer preferences. For example, a company producing a surplus of a product that consumers do not desire is operating productively efficient but lacks allocative efficiency.
What Are the Real-World Implications of Allocative Efficiency vs Productive Efficiency?
The concepts of allocative efficiency and productive efficiency have significant implications for various stakeholders in the economy:
- For consumers, understanding these efficiencies can lead to better purchasing decisions.
- For businesses, optimizing both forms of efficiency can enhance competitiveness and profitability.
- For policymakers, promoting an environment that fosters both efficiencies can lead to improved economic performance.
How Can Policymakers Promote Allocative and Productive Efficiency?
Policymakers can encourage both allocative and productive efficiency through various strategies:
- Implementing regulations that promote fair competition.
- Investing in education and training to enhance workforce skills.
- Encouraging research and development to foster innovation.
Conclusion: The Balance Between Allocative Efficiency and Productive Efficiency
In conclusion, understanding the concepts of allocative efficiency vs productive efficiency is essential for navigating the complexities of economic theory and practice. Both forms of efficiency play critical roles in shaping the economic landscape, influencing everything from resource allocation to consumer satisfaction. By recognizing the importance of both efficiencies and their interaction, stakeholders can work towards creating a more efficient and prosperous economy for all.
You Might Also Like
Exploring The Enigmatic World Of Rumah Perjaka SiteUnraveling The World Of Spider Game Online
Unraveling The Mystery: Which Of The Property Brothers Died?
Exploring The Unique Bond Between Michael Oher And Collins Tuohy
Unraveling The Mysteries: Is Morgan Wallen Single In 2024?
Article Recommendations