DNA replication is a fundamental biological process pivotal for the growth and reproduction of living organisms. It ensures that genetic information is accurately passed on from one generation to the next, maintaining the integrity of life itself. But what makes DNA replication a semi-conservative process? This intriguing question invites us to explore the mechanics of molecular biology, where the strands of DNA undergo a meticulous copying process that is both efficient and reliable.
The semi-conservative nature of DNA replication means that each new double helix contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This method of replication is essential for preserving the genetic blueprint embedded in the DNA. Unlike conservative replication, which would keep the original strands intact while creating entirely new strands, semi-conservative replication allows for a more accurate and efficient transfer of genetic information. Understanding why DNA replication is semi-conservative provides valuable insights into the principles of heredity and genetic fidelity.
As we delve deeper into the question of why DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, we will uncover the intricate mechanisms that facilitate this process. We will examine the role of enzymes, the significance of base pairing, and the implications this method has on genetic stability. By the end of this exploration, the answer to why DNA replication follows a semi-conservative model will become clearer, highlighting its importance in the realm of genetics and molecular biology.
What Does Semi-Conservative Mean in DNA Replication?
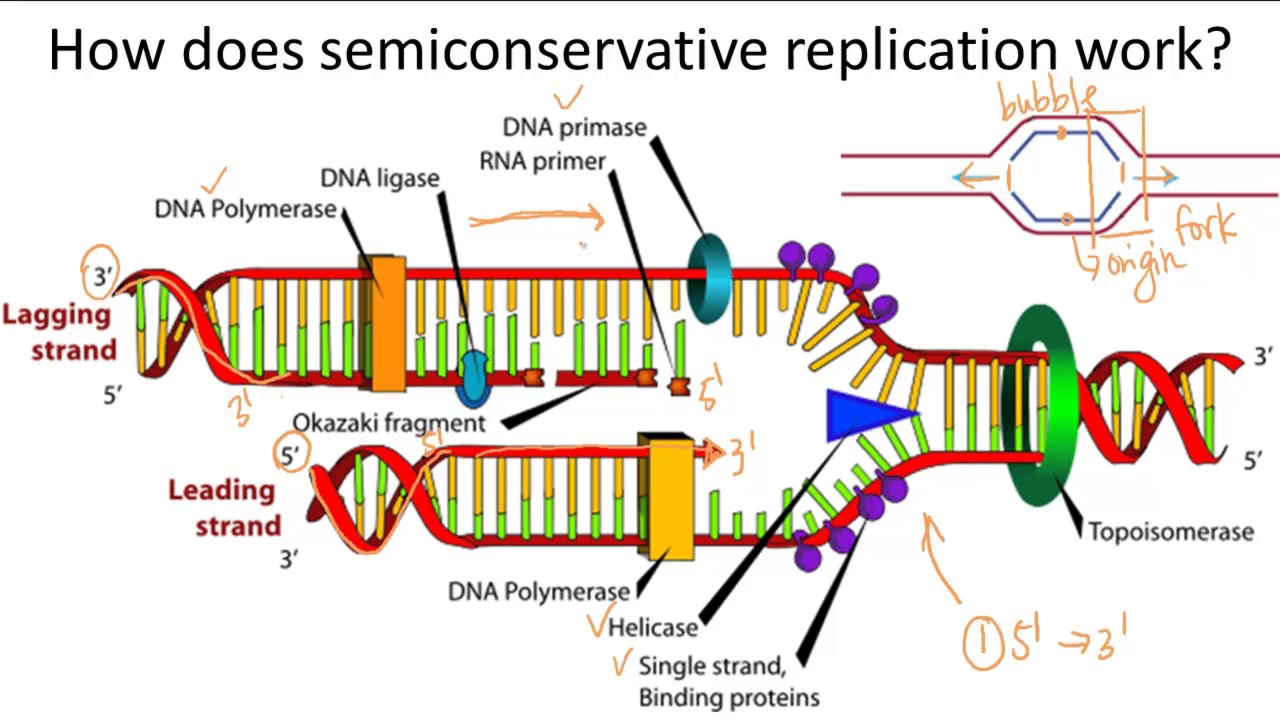
Semi-conservative replication refers to the method by which DNA is duplicated. Each of the two resulting DNA molecules consists of one original (template) strand and one newly synthesized strand. This contrasts with conservative replication, where one of the daughter molecules would contain both original strands while the other would consist of entirely new strands.
Why is DNA Replication Semi-Conservative?
The semi-conservative nature of DNA replication is crucial for several reasons:
- Maintains Genetic Integrity: By using one original strand as a template, the process reduces the likelihood of mutations.
- Enhances Accuracy: The base pairing rules (adenine with thymine, cytosine with guanine) ensure that the new strand is an exact copy of the original.
- Facilitates Quick Replication: The use of pre-existing strands allows for a faster and more efficient copying process.
- Supports Cell Division: It is essential for mitosis and meiosis, ensuring that daughter cells receive identical genetic material.
What Are the Key Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication?
A variety of enzymes play vital roles in the process of DNA replication, including:
- Helicase: Unwinds the DNA double helix.
- DNA Polymerase: Synthesizes the new DNA strand by adding nucleotides complementary to the template strand.
- Ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- Primase: Synthesizes RNA primers that initiate the synthesis of the new DNA strand.
How Does the Process of DNA Replication Occur?
The process of DNA replication can be broken down into several key steps:
- Initiation: The replication process begins at specific sites called origins of replication.
- Unwinding: Helicase unwinds the double-stranded DNA, creating two single strands.
- Priming: Primase synthesizes short RNA primers that provide a starting point for DNA synthesis.
- Elongation: DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, following base pairing rules.
- Termination: Once the entire DNA molecule has been replicated, the process concludes.
What Role Does Base Pairing Play in DNA Replication?
Base pairing is fundamental to the accuracy of DNA replication. The specific pairing between adenine and thymine (A-T) and between cytosine and guanine (C-G) ensures that the new strand is a faithful copy of the original strand. This mechanism not only enhances the fidelity of the replication process but also allows for the correction of errors through proofreading mechanisms that DNA polymerases possess.
Why is Understanding Semi-Conservative Replication Important?
The understanding of why DNA replication is a semi-conservative process has profound implications in various fields:
- Genetics: Insights into genetic inheritance and mutations.
- Medicine: Understanding diseases related to DNA replication errors.
- Biotechnology: Applications in cloning, gene therapy, and synthetic biology.
How Does Semi-Conservative Replication Influence Evolution?
The semi-conservative nature of DNA replication influences evolution by ensuring that genetic variations are accurately preserved and passed on. This fidelity is crucial for natural selection, as it allows beneficial mutations to be inherited while minimizing the risks of deleterious mutations. The stability provided by semi-conservative replication is a cornerstone of evolutionary biology, contributing to the diversity of life we see today.
You Might Also Like
Unlocking The Potential Of Inert Materials: A Comprehensive GuideUnderstanding Gallon Paint Cost: A Comprehensive Guide
Unraveling The Mystery: Does Chloe Betray Lucifer In Season 4?
Bryson Tiller's Journey Through Relationships
Discovering The Allure Of Www.rumah Perjaka
Article Recommendations